June 2, 2022
(press release)
–
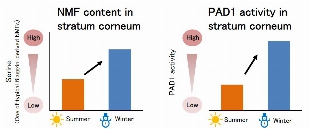
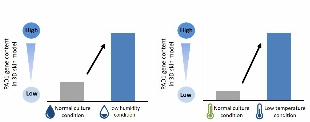
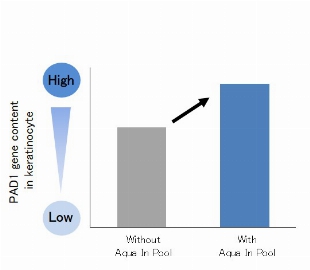
~Its second technology to create beauty in harmonious coexistence with environment and based on the wealth it provides~ Shiseido Company, Limited (“Shiseido”) has revealed that in a dry environment, the skin promotes the production of Peptidyl Arginine Deiminase 1 (PAD1), an enzyme that produces Natural Moisturizing Factor (NMF). This suggests that the skin has the ability to retain moisture, coexisting with the environment. In addition, we have found a new ingredient that enhances PAD1 expression and supports the skin’s moisture retention ability. These findings are expected to be applied to the development of cosmetics that boost the skin’s abilities to adapt and resist to a dry environment. Some of these results were presented at the 46th Annual Meeting of the Japanese Society for Investigative Dermatology held from December 3 to 5, 2021. Figure 1. Environment-adaptive moisture retention ability (image) Research background Our skin has acquired adaptability to the external environment, such as sweating at high temperatures and production of melanin during UV exposure, etc., in the evolution of mankind. However, skin’s adaptive capability to a dry environment caused by low humidity and low temperature has not been fully clarified. Thus, by applying our knowledge and findings on the production pathway of skin’s natural moisturizing factor NMF gathered through more than 40 years of research, we have conducted research to elucidate the skin’s innate adaptation mechanism to a dry environment. Discovering the skin’s ability to create “moisture” to adapt to a dry environment NMF is supplied mainly through the pathways of “filaggrin”, a protein that makes up the skin, and “sweat” and serves as an essential component of moisture retention in the stratum corneum. In this study, we compared the NMF contents between summer and winter in the same individuals and found that filaggrin-derived NMF was more abundant in winter than in summer (Figure 2 left). Then, we further analyzed NMF-producing enzymes in the same individuals in summer and winter in order to clarify the mechanism of seasonal variation of filaggrin-derived NMF and found that the activity of PAD1, which promotes NMF production, was also increased in winter. In addition, through our culture experiments on a 3D skin model under controlled temperature and humidity conditions, we confirmed that PAD1 was upregulated in a low-humidity and low-temperature environment. With these results, it was revealed that skin enhances its moisture retention ability by boosting the production of NMF-producing enzyme PAD1 in order to adapt to a dry environment caused by low humidity and low temperature. Figure 2. Filaggrin-derived NMF and activity of NMF-producing enzyme PAD1, both increase in winter. Figure 3. PAD1 gene content increased in low-humidity and low-temperature environment. Discovery of an ingredient promoting PAD1 expression After searching for ingredients that promote the expression of PAD1, a key enzyme for environment-adaptive moisture retention, we discovered that “Aqua In Pool”, an ingredient uniquely developed by Shiseido, has the effect of inducing PAD1 production. In addition, we also identified several plant extracts with similar effects. These ingredients are expected to help further enhance the skin’s adaptive ability to a dry environment. Figure 4. PAD1 gene content increased by Aqua In Pool Future prospects While changes in the natural environment become increasingly noticeable worldwide, we will further advance our technologies based on the new idea of “accepting the environment and living in harmony”. Following the first phase of our technology for coexistence with ultraviolet light and then the environmental factors such as low humidity and low temperature that we revealed in this research, we will continue to take on new challenges to develop technologies that make positive, beneficial use of various environmental factors and deliver beauty innovations to people around the world with the aim of realizing our corporate mission, “BEAUTY INNOVATIONS FOR A BETTER WORLD”. *The content of the release is correct as of the time of release, but please note that it may in some cases differ from the latest information.
We, at Shiseido, are aiming to realize beauty in positive coexistence with the environment through the Premium/Sustainability approach of our unique R&D philosophy, “DYNAMIC HARMONY”. While focusing on the skin’s response mechanism to environmental changes, we will be engaged in the development of the technologies that convert natural environmental factors such as humidity and temperature into the power of beauty, following the announcement of UV conversion technology* in November, 2021.
*Shiseido develops innovative technology to convert ultraviolet light into light that brings about beneficial effects on the skin (2021)
https://corp.shiseido.com/en/news/detail.html?n=00000000003256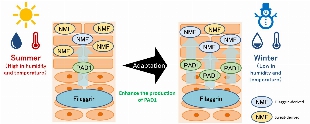
* All content is copyrighted by Industry Intelligence, or the original respective author or source. You may not recirculate, redistrubte or publish the analysis and presentation included in the service without Industry Intelligence's prior written consent. Please review our terms of use.




